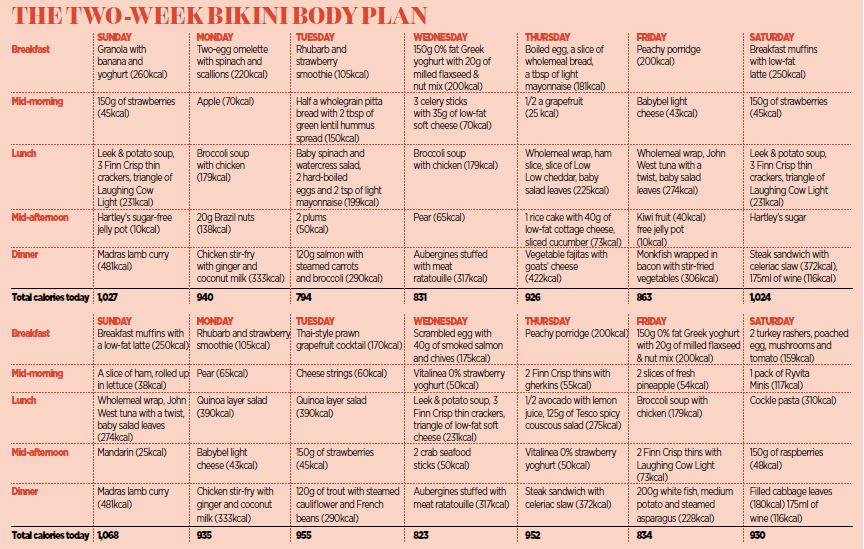
2 Week Beach Diet: This plan offers a structured approach to achieving a desired physique within a short timeframe. It involves a combination of dietary restrictions, focused exercise, and careful consideration of potential risks. Understanding the principles of this diet, including its nutritional aspects and potential drawbacks, is crucial for safe and effective implementation.
This guide explores the 2-week beach diet concept in detail, providing a sample meal plan, workout routine, and crucial information regarding potential risks and alternative, more sustainable approaches to weight management. We’ll delve into the nutritional benefits and drawbacks, emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before embarking on any rapid weight loss plan.
Alternative Approaches to Achieving Beach Body Goals
While a focused diet can be helpful for short-term goals, lasting changes require a holistic approach to health and well-being. Sustainable weight loss and a “beach body” are best achieved through lifestyle changes that prioritize long-term health rather than quick fixes. This section explores alternative strategies for achieving your fitness goals.
Healthy and Sustainable Weight Loss Strategies
Sustainable weight loss isn’t about rapid weight shedding; it’s about making gradual, healthy changes that you can maintain over time. This table outlines several effective strategies:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. | Improved energy levels, better digestion, reduced risk of chronic diseases, sustained weight management. | Requires careful planning and preparation; may require adjustments to social eating habits. |
| Regular Exercise | Engaging in a combination of cardiovascular exercise (like running or swimming) and strength training (like weightlifting or bodyweight exercises) most days of the week. | Improved cardiovascular health, increased muscle mass, boosted metabolism, stress reduction. | Requires time commitment and may lead to muscle soreness initially. |
| Mindful Eating | Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring your food without distractions. | Improved digestion, reduced overeating, increased awareness of food choices. | Requires conscious effort and practice; may be challenging in social situations. |
| Stress Management | Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. | Reduced cortisol levels (a stress hormone linked to weight gain), improved sleep, better overall mental health. | Requires consistent effort and finding techniques that work for you. |
Incorporating Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting healthy eating habits is a journey, not a destination. Small, consistent changes are more effective than drastic overhauls. Start by focusing on gradually increasing your intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Planning your meals ahead of time and preparing healthy snacks can also be helpful. Remember that occasional treats are perfectly acceptable as part of a balanced lifestyle.
Benefits of Focusing on Overall Health and Well-being
Prioritizing overall health and well-being offers far more than just a desirable physique. It leads to improved energy levels, better sleep, stronger immunity, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and enhanced mental clarity. This holistic approach contributes to a higher quality of life, making you feel better both inside and out. The focus shifts from a temporary aesthetic goal to a sustainable lifestyle that supports long-term health and happiness.
Reliable Nutrition and Fitness Information Resources
Reliable information is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. Consult registered dietitians or certified personal trainers for personalized guidance. Reputable organizations like the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the American College of Sports Medicine provide evidence-based information on nutrition and fitness. Government health websites (such as the CDC and NIH) are also excellent sources of trustworthy data. Always be critical of information found online and prioritize sources backed by scientific research.
Illustrative Examples of Food Choices
Choosing the right foods is crucial for a successful beach diet. The following examples showcase nutritious and delicious options that align with a high-protein, vegetable-rich approach while emphasizing portion control. Remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual caloric needs and activity level.
High-Protein Breakfast
A high-protein breakfast jumpstarts your metabolism and keeps you feeling full, preventing mid-morning snacking. A great example is a Greek yogurt parfait. Imagine a base of ½ cup plain, nonfat Greek yogurt, layered with ¼ cup mixed berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), a sprinkle of chia seeds (1 tablespoon) for added fiber and omega-3s, and a drizzle of honey (1 teaspoon) for sweetness. This breakfast provides a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, keeping you energized throughout the morning.
Healthy Vegetable and Lean Protein Lunch
A balanced lunch should focus on vegetables and lean protein to promote satiety and provide essential nutrients. Consider a large salad with 4 ounces of grilled chicken breast or salmon. The salad should be packed with a variety of colorful vegetables like spinach, bell peppers, cucumbers, and carrots. A light vinaigrette dressing, made with olive oil and lemon juice, adds flavor without excessive calories. This meal is high in protein, fiber, and vitamins, supporting your beach body goals.
Balanced Dinner with Portion Control
Visualize your dinner plate divided into three sections. One section (approximately ½ of the plate) is filled with lean protein, such as 4 ounces of baked cod or grilled tofu. Another section (approximately ¼ of the plate) is dedicated to complex carbohydrates, such as ½ cup of quinoa or brown rice. The remaining section (approximately ¼ of the plate) is filled with a colorful array of steamed vegetables, such as broccoli, asparagus, and green beans. This visual representation helps ensure appropriate portion sizes, preventing overeating while providing a balanced meal.
Healthy Snack Option
A healthy snack should be both satisfying and low in calories. A perfect example is a small handful (about 1/4 cup) of almonds. Almonds are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and protein, which contribute to feelings of fullness and sustained energy. They also provide essential vitamins and minerals. This snack helps curb cravings and prevents overeating during meals.
Closing Notes
Ultimately, the 2-week beach diet, while potentially effective for short-term weight loss, should be approached cautiously. The focus should shift from rapid results to establishing sustainable, healthy habits for long-term well-being. Prioritizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and overall health will yield far more rewarding and lasting results than any quick-fix solution. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new diet or exercise program.